c1 esterase inhibitor deficiency
Some affected individuals with clear depression of C1 esterase inhibitor do not have clinical manifestations of disease. Adults or elderly patients are most commonly affected.

Ace I Moa Pharmacology Vasoconstriction Nursing Tips
C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency also known as hereditary angioedema results in the unchecked production of the vasodilator bradykinin.

. During attacks patients usually develop detectable levels of free C1 esterase which cannot be found in the circulation of normal individuals. Both conditions lead to recurrent angioedema that can be life threatening when the larynx is involved hereditary angioedema HAE. These skin conditions typically involve the legs hands face upper respiratory tract as well as gastrointestinal tract. CAS PubMed Article Google Scholar 52.
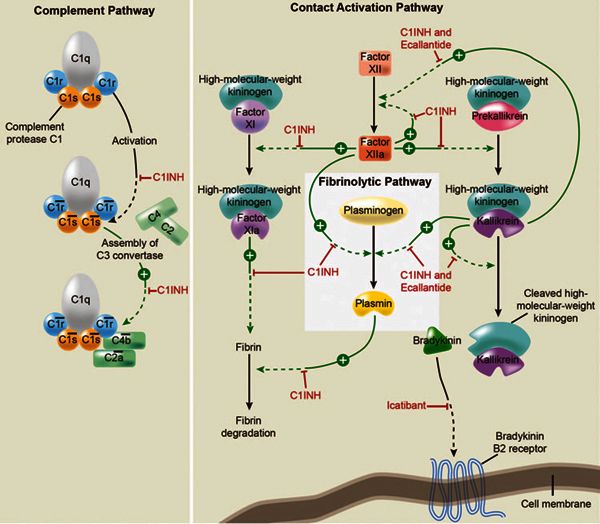
This increase in bradykinin leads to an increase in smooth muscle relaxation in the walls of blood vessels and resultant edema in the hands feet gastrointestinal tract and in severe cases the larynx. The function of C1 inhibitor is to regulate the fluid leakage from blood vessels and prevent any excess fluid buildup edema. Intravenous administration of reconstituted plasma-derived C1-inhibitor human replaces the C1-inhibitor regulatory protein. 5 Lack of C1 INH leads to uncontrolled activation of the classical pathway of complement and is thought to result in the.
Acquired C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency is a rare condition associated with autoimmune or low-grade lymphoproliferative disorders. Hereditary Angioedema C1 Esterase Deficiency Background. Acquired C1 inhibitor deficiency may occur with B-cell lymphomas and some autoimmune diseases. Presents as recurrent bouts of angioedema involving the extremities face oropharynx larynx.
Hereditary angioneurotic oedema is an autosomal dominantly inherited condition caused by a deficiency of C1 esterase inhibitor 1. C1 esterase inhibitor is the main regulator in the activation of. C1 the first component of the classical pathway of complement exists in serum as a macromolecular complex containing one C1q two C1r and two C1s molecules. A hereditary disorder that results in angioedema without urticaria.
Acquired C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency. Acquired C1 inhibitor deficiency also known as acquired angioedema AAE hereditary angioedema HAE hereditary angioneurotic edema. Activation of this macromolecule leads to cleavage of C1s to produce C1s also called C1. Hereditary angioedema HAE caused by C1-esterase inhibitor deficiency is an autosomal-dominant disease resulting from a mutation in the C1-inhibitor gene.
Hereditary angioedema otherwise known as C1 esterase deficiency is defined by recurrent episodes of angioedema without urticaria or pruritus. C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency. The diagnosis is suspected when patients present with recurrent angioedema and low serum levels of C4 with normal levels of C3. Acquired angioedema due to deficiency of C1 esterase inhibitor also called acquired angioedema and abbreviated C1INH-AAE is a rare syndrome of recurrent episodes of angioedema without urticaria which is associated with B cell lymphoproliferative disorders in some patients.
3 4 In 1972 an aquired form of C1 INH deficiency was first reported. C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency is the most common complement deficiency antigenic or functional and is transmitted as an autosomal dominant disorder resulting in hereditary angioneurotic oedema. HAE is characterized by recurrent attacks of intense massive localized subcutaneous edema involving the extremities genitalia face or trunk or submucosal edema of upper airway or bowels. The resultant over-stimulation of this system leads to the production of inflammatory anaphylatoxins which affects the flow of body fluids between the vascular system and body tissues.
There are two mechanisms which can lead to this condition. Consumption due to complement activation or rarely due to an. Type I hereditary angioedema HAE 123. Angioedema typically affects the skin or mucosal tissues of the upper.
Most cases of acquired C1-inhibitor deficiency are associated with an underlying B-cell disorder ranging from auto-immune anti-C1-inhibitor auto-antibodies to lymphoproliferative disease usually a low grade or splenic marginal zone lymphoma. HAE type I is primarily caused by a deficiency in blood proteins C1 esterase inhibitors which normally suppress activation of the complement system. C1INH deficiency or dysfunction results in low levels of C4 because the C1 complex normally cleaves C4 as part of classical complement pathway and this is exaggerated if C1INH is deficient. Hereditary angioedema otherwise known as C1 esterase deficiency is defined by recurrent episodes of angioedema without urticaria or pruritus.
Early onset of symptoms may predict a more. Tekin ZE Yener GO Yuksel S. HAEGARDA is for subcutaneous use after reconstitution only. Hereditary angioedema and acquired C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency specifically involve the complement system.
Accounts for about 85 of patients. The diagnosis of C1-INH-HAE is often delayed for years. C1 Esterase Inhibitor Deficiency. These skin conditions typically involve the legs hands face upper respiratory tract as well as gastrointestinal tract.
Hereditary angioedema HAE is a rare condition arising from a genetic deficiency of C1-esterase inhibitor also called C1-inhibitor a regulator of inflammatory pathways. HAEGARDA C1 Esterase Inhibitor Subcutaneous Human is a plasma-derived concentrate of C1 Esterase Inhibitor C1-INH indicated for routine prophylaxis to prevent Hereditary Angioedema HAE attacks in patients 6 years of age and older. PubMed Article Google Scholar 53. Hereditary C1 inhibitor deficiency indistinguishable clinically from type II HAE.
Tran JP McCracken JL Morsy A Gonzalez EB. C1 esterase inhibitor is a protein which is produced mainly in the liver and to some extent by activated Monocytes and other cell types. What is C1 esterase inhibitor deficiency. The time between the onset of symptoms and diagnosis averages 85 years.
Hereditary C1 inhibitor deficiency. The genetic defect is due to the heterozygous deficiency of C1-Inh that is transmitted as an autosomal dominant trait. Acquired angioedema in juvenile systemic lupus erythematosus. This disorder can lead to airway.
C4 and C2 the substrates of C1 esterase are chronically depressed in most patients. Due to autosomal dominant deficiency or dysfunction of C1 esterase inhibitor release of vasoactive mediators vascular permeability edema formation. Etiology and Risk Factors of C1 Esterase Inhibitor Deficiency The cause for C1 inhibitor deficiency is a genetic mutation of the C1 inhibitor gene which causes decreased C1 inhibitor production. C1-inhibitor deficiency can be inherited or acquired.
2 The pathophysiologic basis of HAE deficiency of C1 esterase inhibitor which is also called C1 inhibitor C1 INH was postulated in the early 1960s.

C1 Esterase Inhibitor Deficiency Dysfunction C1 Inhibitor Mario Characters Character

Bradykinin Induced Angloedema Emergency Medicine Nursing School Scholarships Clinical Nurse Specialist

Cilnidipine An L N Type Calcium Channel Blocker Changes The Circulating Angiotensin 1 7 Angiotensin Ii Ratio Calcium Channel Blockers Channel Calcium


Posting Komentar untuk "c1 esterase inhibitor deficiency"